RFID in Aviation

![]()
Follow OATSystems Aerospace Manufacturing and Supply Chain content on ![]()
Stay updated on new content via RSS ![]()
![]()
Airbus Extends RFID Part Marking to All Aircraft Families
 In a recent press release, Airbus announced that they will be extending their A350 Part Marking program to all aircraft. All life vests and seats will have RFID tags by 2013. One reason? Safety and efficiency in turnaround operations. Life vests have expiration dates that need to be checked regularly – an RFID tag on each vest allows a crew member to walk down the aisle with an RFID reader, taking inventory and uncovering soon-to-expire equipment in minutes (instead of hours spent removing vests stored under seats and reading expiration dates).
In a recent press release, Airbus announced that they will be extending their A350 Part Marking program to all aircraft. All life vests and seats will have RFID tags by 2013. One reason? Safety and efficiency in turnaround operations. Life vests have expiration dates that need to be checked regularly – an RFID tag on each vest allows a crew member to walk down the aisle with an RFID reader, taking inventory and uncovering soon-to-expire equipment in minutes (instead of hours spent removing vests stored under seats and reading expiration dates).
RFID Journal details the part marking announcement here. OATSystems has worked closely with Airbus since 2008 to RFID-enable the A380 supply chain and to roll out part marking programs for the Airbus A350, where serialized, line-maintainable components are marked with RFID High Memory tags. For more information on the Airbus A350 Part Marking Program, and supplier packages, click here.
![]()
Automating Composites Manufacturing Processes with RFID
In a Composites Manufacturing Online blog post, OAT Systems Engineering Director Anurag Nagpal outlines a recent RFID materials management project at an aerostructures manufacturer. The manufacturer used OATSystems' software integrated with their Solumina material management system and Xerafy ruggedized tags to manage temperature-sensitive composite prepreg material from shipping dock receipt to storage freezers to layup and autoclave processes.
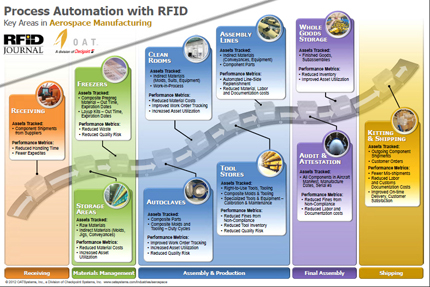
Composite prepreg (commonly used for fabricating curved structural components, is a perishable material that must be transported, stored and monitored at sub-zero temperatures. Structural properties of prepreg can degrade once recommended "freezer out time" has elapsed. Tracking freezer out-time in a systematic manner is time consuming and error prone, often leading to questionable material being discarded as scrap, RFID-enabled tracking can result in significant cost savings. . Since the on-hand inventory of prepreg for a manufacturer can comprise close to $1 million at any time, trimming the percentage of scrap material can result in significant cost savings. The diagram below illustrates multiple areas where composite manufacturing processes can be automated with RFID:

![]()
Work-in-Process Tracking is More Complex in Aerospace and Defense
RFID-enabled WIP Tracking improves manufacturing efficiency in many industries – chemicals, automotive, consumer goods. Complex Aerospace and Defense manufacturing processes can realize additional benefit from RFID automation. The complexity lies in 3 areas: Composites Manufacturing (which creates material handling challenges), Tooling Proliferation (which includes composite tooling, specialized jigs, conveyances and production equipment) and Inter-Facility WIP Tracking (as noted in the paragraph below). For a recent RFID in Aerospace and Aviation Virtual Event, OAT and RFID Journal created a poster-sized Infographic which describes key areas for RFID Process Automation in Aerospace and Defense manufacturing with corresponding performance metrics. Download the Infographic here or by clicking on the thumbnail below.
![]()
For Aerospace Manufacturers, WIP Tracking = Inter-Facility Tracking
Aerospace Manufacturers must manage production processes across multiple facilities, which adds a new dimension to Work-in-Process Tracking. More than tracking assembly from work station to work station, WIP Tracking needs to incorporate logistics and conveyance tracking processes for inter-facility shipments.

Automating logistics processes vs. traditional WIP tracking with RFID actually simplifies deployment since shipments are tracked by customer order instead of the individual component level. We've found that RFID Inter-Facility Tracking projects significantly improve on-time delivery for manufacturers. An added bonus is that most projects pay for themselves within months of initial deployment by eliminating costly expedites, rework and customer discounts.
![]()
Extreme RFID – Tracking from Freezer to Layup to Autoclave
 The most recent aircraft programs, including the Airbus A350, Boeing 787 Dreamliner and Bombardier C Series are achieving fuel efficiency through lighter, stronger composite materials. This poses both new opportunities and challenges for Aerospace Manufacturers, who must add new materials management, fabrication and inspection processes to their current operations. RFID technology can help automate and error proof composite manufacturing processes.
The most recent aircraft programs, including the Airbus A350, Boeing 787 Dreamliner and Bombardier C Series are achieving fuel efficiency through lighter, stronger composite materials. This poses both new opportunities and challenges for Aerospace Manufacturers, who must add new materials management, fabrication and inspection processes to their current operations. RFID technology can help automate and error proof composite manufacturing processes.
OAT and Xerafy produced a short video illustrating RFID tracking from freezer to layup to autoclave, based on recent customer engagements.
Click here to view the video. Click here for more detailed information and registration for the OAT-Xerafy Extreme RFID webinar recording, slides and Extreme RFID deployment guides.
![]()
Airbus A350 Supplier Program – RFID Software Considerations
 Since the launch of Airbus A350 Supplier Packages at RFID Journal Live 2011, suppliers have selected and tested high memory tags and mounting options. Their next steps are to document processes for managing RFID sensor data and to integrate it with WIP Tracking systems – which is beyond the scope of high memory tag "starter kits". Based on supplier requests for upgrading tag kits, A350 Supplier Packages now include a Software-Only option, which includes OAT's enterprise-tested software, along with installation and consulting services.
Since the launch of Airbus A350 Supplier Packages at RFID Journal Live 2011, suppliers have selected and tested high memory tags and mounting options. Their next steps are to document processes for managing RFID sensor data and to integrate it with WIP Tracking systems – which is beyond the scope of high memory tag "starter kits". Based on supplier requests for upgrading tag kits, A350 Supplier Packages now include a Software-Only option, which includes OAT's enterprise-tested software, along with installation and consulting services.
![]()
Extreme RFID: Tracking Machinery and Tooling in Challenging Environments
 The newest generation of ruggedized RFID tags can extend visibility to "extreme" asset tracking processes in A&D –including tooling tracking, WIP tracking and equipment management, from freezer to autoclave to maintenance hangar. OATSystems and Xerafy recently co-hosted a webinar to walk through deployment options and use cases for materials management and WIP Tracking for composite materials and Asset Tracking for tooling, jigs, conveyances and specialized equipment, along with considerations for selecting ruggedized RFID tags. Get further information and registration for the on-demand webinar recording, slides and Extreme RFID deployment guides.
The newest generation of ruggedized RFID tags can extend visibility to "extreme" asset tracking processes in A&D –including tooling tracking, WIP tracking and equipment management, from freezer to autoclave to maintenance hangar. OATSystems and Xerafy recently co-hosted a webinar to walk through deployment options and use cases for materials management and WIP Tracking for composite materials and Asset Tracking for tooling, jigs, conveyances and specialized equipment, along with considerations for selecting ruggedized RFID tags. Get further information and registration for the on-demand webinar recording, slides and Extreme RFID deployment guides.
![]()
Best Practices Guide for RFID & RTLS in Aerospace and Defense
 Aerospace manufacturers, defense contractors and MRO providers are deploying RFID and RTLS technology for different use cases and business processes. What do successful deployments have in common? And where does process automation provide the biggest payoff?
Aerospace manufacturers, defense contractors and MRO providers are deploying RFID and RTLS technology for different use cases and business processes. What do successful deployments have in common? And where does process automation provide the biggest payoff?
OATSystems recently presented at an RFID Journal webinar to discuss real-world A&D RFID deployments in WIP tracking, tool tracking, part marking, jig tracking, audit & attestation, and other process areas. RFID Journal has posted links to the presentation along with an RFID/RTLS Deployment Guide for Aerospace and Defense (with process flow diagrams and integration options for Manufacturing, Sourcing, Logistics and MRO operations, on their website.
Presentation: http://www.rfidjournalevents.com/virtual_agenda.php?eid=18
Deployment Guide: http://www.rfidjournalevents.com/guide.php
![]()
7 Reasons for Automating Tool Tracking with RFID
For many manufacturers (especially in Aerospace, Defense and Industrial Machinery), a missing tool on the shop floor can be more costly than a missing component part. Most specialized tools and tooling are single-sourced, custom made, and difficult to replace. Freestanding production tooling (e.g. a laser scriber, a lift table) or composite tooling (hard or soft molds) may take weeks to replace, causing schedule and program delays.
In this context, the word “tool” is defined as devices used to perform work in the manufacturing process (WIP) as well as fixtures, molds and other indirect materials used to make and transport WIP (often called “tooling”) in daily manufacturing operations.
Automating Tool Tracking with RFID and RTLS technology can yield the following benefits:
1. Labor savings: By automating tool tracking, manufacturers can dramatically reduce employee time spent on tool check-in and check-out. Improved tracking also enables increased storage of tools at the point of use, reducing employee time spent at centralized tool facilities. This is particularly important in Aerospace and Defense, where an intra-facility walk may be measured not in yards, but in miles.
2. WIP visibility: Real-time insight into the tooling that carries costly WIP helps manufacturers better understand their key operational metrics such as excess inventory or unexpectedly long process cycle times, enabling investigation and reduced inventory carrying costs. WIP often represents millions of dollars in working capital – streamlining the capital allocation can lead to immediate and significant cost savings.
3. Tool cost savings: With greater visibility into tool usage, manufacturers can purchase and deploy fewer tools for usage and spares inventory, along with increasing overall asset utilization.
4. Improved Foreign Object Damage (FOD) Management: Better tool visibility enables better FOD control and risk mitigation, enhancing procedural and training efforts.
5. Audit compliance: Government contractors are subject to their own internal audits as well as DCMA and DCAA audits, so they must document the location of company-owned and government-owned tools, and demonstrate appropriate right-to-use. If not, they face the high costs of a Corrective Action Request (CAR) and risk progress payment delays and fines. RFID-enabling tool tracking greatly reduces these risks and costs, by immediately locating program-specific tools at the time of audit, and by alerting the tool operator before improper use of a right-to-use tool.
6. Calibration: When tools cannot be located, they are frequently listed as missing, although in reality they may be in use on the shop floor. As a result, a percentage of tools that require calibration may be out of spec, leading to process exceptions that cause quality issues. RFID-enabled tool tracking ensures that these tools can be located and calibrated according to the required schedule.
7. ERP efficiency: Real-Time Tool Tracking data may inform an ERP, Program Management and MRO system, making end-to-end manufacturing and logistics processes more efficient. For instance, if a tool is associated with a specific step in the assembly process, the WIP Tracking system can be informed when the tool is checked out and update the production status.
![]()
High Memory RFID Tags
Aerospace OEMs and MRO providers are increasingly adopting high-memory RFID tags for digitally storing part manufacturing and maintenance history for the life of an aircraft. Boeing recently announced an alliance with Fujitsu for maintenance operations and Airbus announced RFID tracking of component parts for the A350 aircraft from the point of manufacture The increased memory capacity of high-memory chips from companies like Tego, provides the ability to store point-of-use maintenance data for A&D manufacturers, logistics and service providers across the value chain.
OAT is advising multiple aerospace suppliers (including A350 suppliers subject to Airbus’ part marking initiative), on high memory tags. Tag options vary based on component materials (where a tag may be bolted, sewn, attached with adhesive), pressurized/unpressurized environments (which may require ruggedized tags/secure chips) and component life (which can range between 5 and 40 years and would need to store corresponding maintenance history). As of RFID Journal Live 2011, ruggedized memory tags are now available from vendors such as Confidex, Xerafy, MAINtag, RFID Tag Source, Marubeni and others for components as diverse life vests to landing gear. Now that tag technology has matured, the next step for suppliers is planning how to automate part marking processes and use part history data to improve manufacturing efficiency and quality within their own four walls.
![]()
Airbus’ Enterprise RFID Strategy Reaps Rewards
A February 2011 article in RFID Journal, Airbus Leads the Way, details how the Aerospace OEM defines best practices for the industry. Airbus’ Value Chain Visibility Program (aka supply-chain wide RFID program) consists of 20+ projects in sourcing, logistics, manufacturing and aftermarket services. The company has realized millions of euros in cost savings through process visibility, primarily into Work-in-Process, Indirect Materials (such as tools, specialized equipment) and Work Orders.
Considering the capital-intensive nature of Aerospace Manufacturing, it makes fiscal sense to track assets with the level of precision that RFID and RTLS provide. Airbus has made visibility a strategic, integrated initiative across multiple business functions, geographies, facilities and partnerships, enabling them to maximize both cost savings and competitive advantage.
![]()
Managing Composite Tooling
Composite manufacturing has evolved significantly in the past decade, but many manufacturers are using 20th century methods to track composite tooling. Keeping track of hard and soft tooling in a cavernous facility can be challenging, due to:
- A myriad of sizes and materials – which are unwieldy to manage with tool control foam or traditional tool cribs
- Special handling and usage constraints for molds, which can be subjected to extreme temperatures in a freezer or autoclave
- Contractual requirements which state that specific tooling needs to be available for decades after initial manufacture
RFID is well-suited to tracking the location, calibration, maintenance and usage cycles of composite tooling, improving asset utilization while minimizing risk.
OAT
SOLUTIONS SUPPORT: Barcode - Passive RFID - Active RFID - Ultra Wide Band RF (UWB) - Wi-Fi - RTLS - RFID-enhanced EAS - Location Servers - GPS - Application Sensors (e.g. Stack Lights, PLCs, alarms...) |
||
| Bell Helicopter's On-Time Delivery Rate Climbs Higher The aircraft manufacturer is managing the movement of parts from a central warehouse to 8 North American production locations, using an RFID solution from OATSystems. |
| RFID Journal Article: RFID Takes Wing at Composite Aircraft Components Plant A U.S. aircraft parts manufacturer has adopted an RFID solution from Xerafy and OATSystems to track composite materials and molds exposed to extreme temperatures during storage and production. |

On-Demand Webinar:
Real-time
Visibility for SAP in Aerospace & Defense







 OAT Foundation Suite
OAT Foundation Suite